MATERIALS TESTING
Chemical
We are ready to provide you with advice or a quote.
Send us an enquiry here or call 060 727 8002.
Our accredited facilities are equipped to perform a wide range of chemical tests related to aggregates. These tests ensure the quality of designs for roadworks and concrete.


Chemical
SERVICE OFFERING
01
Organic Impurities
This test is done to determine the short-term retardation and long-term deleterious effects of organic impurities.
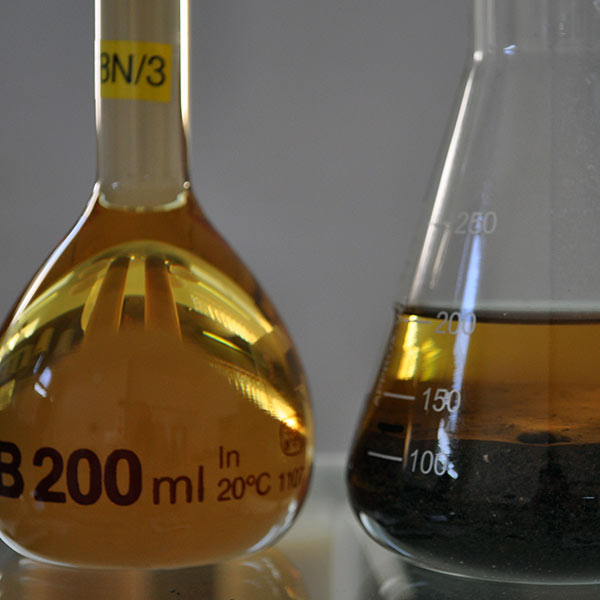

02
Chloride Content
Specifies the determination of the chloride content in aggregates which can have a negative binding effect in some construction applications.
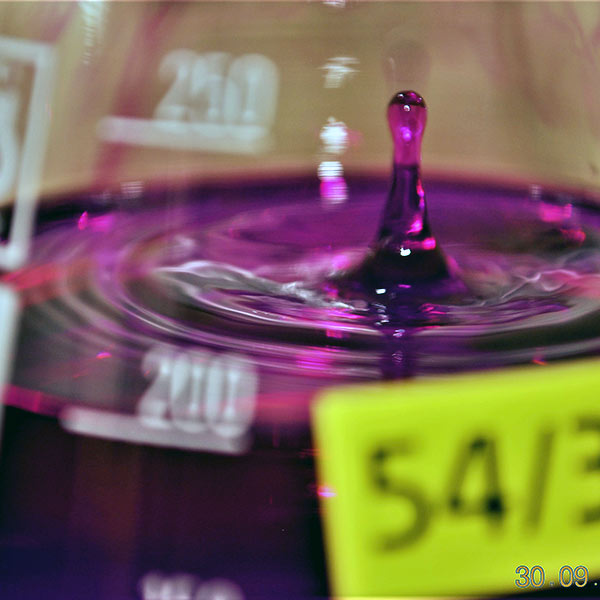

03
Water Soluble Salt Content
This standard specifies a method for determining the total water-soluble salt content of fine aggregates and of fines in aggregates for base courses.

04
Deleterious Clay Content
This method determines whether the clay content of the fines of an aggregate contains deleterious swelling or active clay minerals.
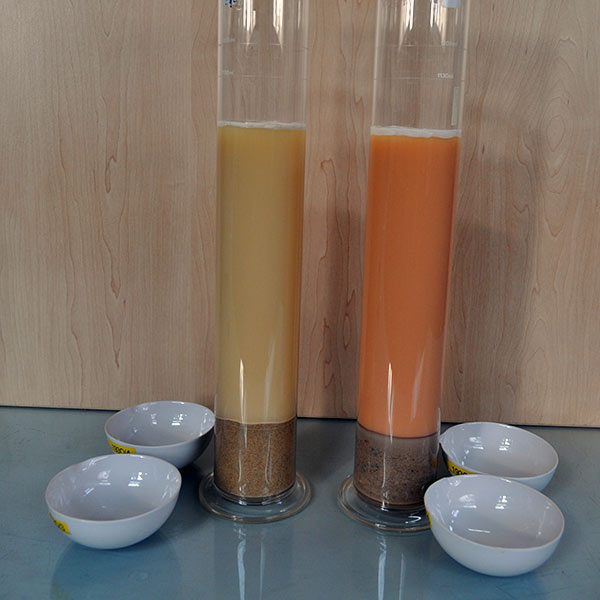

05
Initial Stabilizer Content
Determines the percentage of stabilizer that will first be absorbed by material to neutralize acidity levels before stabilizing takes effect.
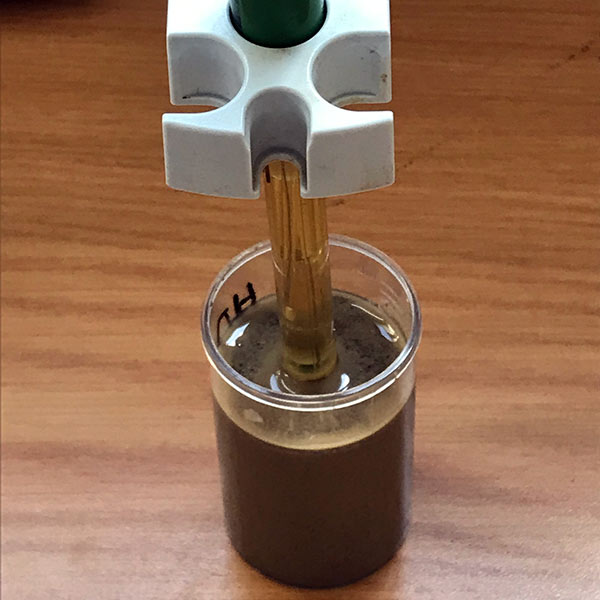

06
Moisture in Asphalt
Used to determine the percentage moisture in a freshly mixed hot mix asphalt (HMA) mix.
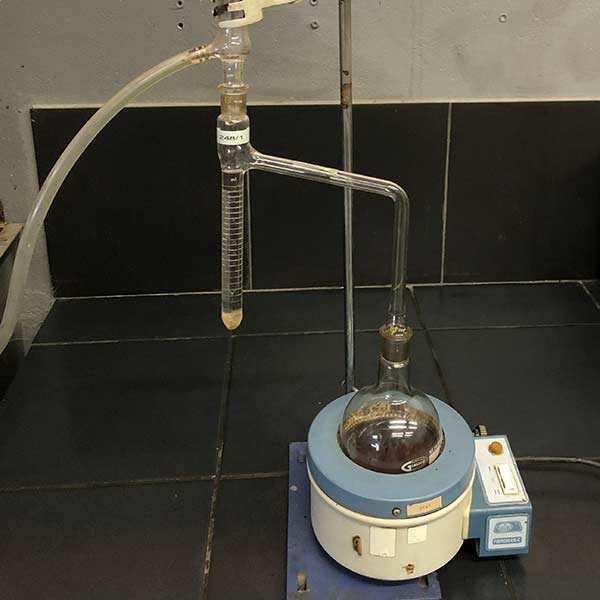

07
Plasticity index Hydrometer test
To determine the particle size distribution of materials to detail the silt and clay percentages.
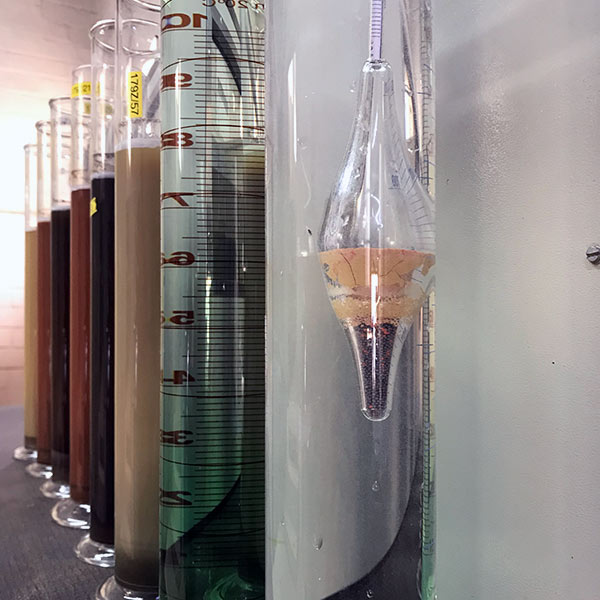

08
Rock Durability Using 10% FACT
Used to determine the strength of the aggregate sample after it has been exposed to a weathering agent.

09
Back-titration
To determine the percentage of stabilizer added during the construction phase to assess design and proper mixing.

10
Particle & Relative Density
The ratio of mass to the mass of an equal volume of water, which defines the weight or density of a material.

11
Methylene Blue
Determines whether the clay content of the fines of an aggregate contains deleterious swelling clay minerals which could adversely affect the quality of the asphalt mix.